Environment as art
Courtney Leonard brings Long Island's Indigenous tradition into focus
An original and compelling voice in contemporary art, Courtney M. Leonard’s artistic perspective takes root in her heritage as a member of the Shinnecock Nation.
Her work amplifies Indigenous knowledge and expresses reverence for the earth and sea while advocating for their protection.
Trained as a ceramic artist, Leonard — who received an advanced degree from Rhode Island School of Design — has evolved her practice to reflect her many interests and pursuits, all in an effort to investigate narratives of cultural viability.
A sculptor, painter and filmmaker in addition to her calling as a ceramicist, Leonard is known for her immersive installations that immediately command attention.
Now her art comes into focus in the first retrospective of her work, “Courtney M. Leonard: Logbook 2004-2023” at the Heckscher Museum of Art, which also is her first solo museum exhibition in the New York metro region.
“Her work is extremely beautiful and visually engaging,” says Heckscher Museum curator Karli Wurzelbacher. “It’s so well-made and deeply meaningful. So many important concepts are embedded within each piece.”
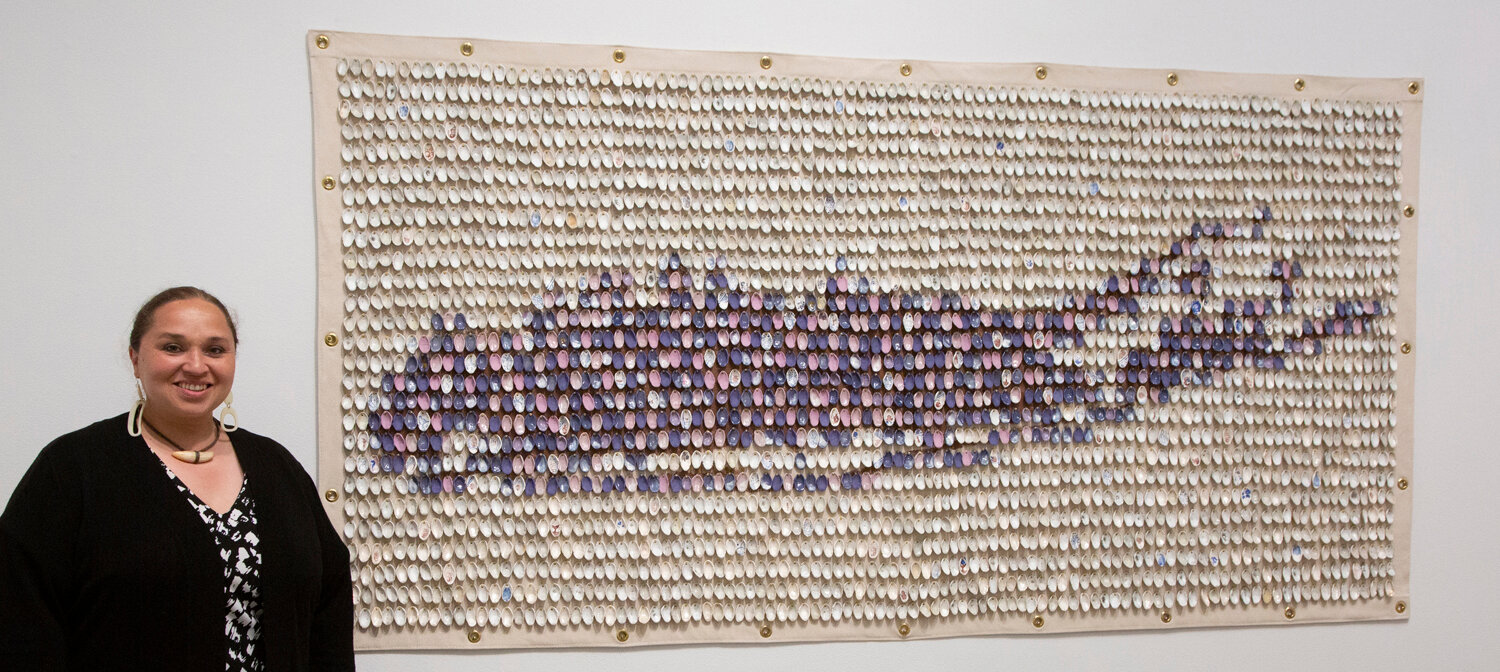
The two dozen pieces on view take over three of the museum’s galleries. Of particular note is the debut of her significant new work commissioned by the museum for its permanent collection. Titled “Contact 2,023…,” the approximately eight-foot-long wall hanging focuses on the moment of colonial contact on Long Island, by mapping the contours of the island with thousands of individual clay thumbprints resembling shells.
Sewn onto a cotton canvas with artificial sinew, each thumbprint becomes a “maker’s mark” indexing the artist’s contact with the earth.
“It’s one amazing work with over 1,000 components,” Wurzelbacher notes.
This monumental creation is a sister piece to two other artworks in Leonard’s Contact series. The two earlier works both map New York state. She created the first, “Contact 1,609… (2009),” on the 400th anniversary of Henry Hudson’s “discovery” of Manhattan and what is now called the Hudson River. It is co-owned by the Los Angeles County Museum of Art and The Autry Museum of The American West in Los Angeles. The second, “Contact 2,021… (2021),” was recently on view at the Metropolitan Museum of Art and will next be shown at the New York Historical Society beginning in August.
Another important exhibit component extends Leonard’s ongoing project Breach, which she began in 2014. Conceived on the model of records kept by 18th century whaling ships, each “logbook” of Breach records — in ceramic, paint and video — one year of the artist’s experiences of “environmental fragility, shifting adaptations, and/or the ability to simply become anew.”
A single installation contained in an entire gallery, Breach: Logbook 23|Alluvion takes its name from a legal term meaning the action of the sea or a river in forming new land by depositing sediment. Connecting the concepts of erosion and alluvion, Leonard explains: “The purple and white of the quahog shell are formed by the water and minerals of a specific place. Alluvion speaks to the history of land, water, place, and to the displacement or disruption from loss of land due to erosion or imposed law. Yet it also speaks to the resiliency of our Shinnecock people and of our shoreline to heal itself.”
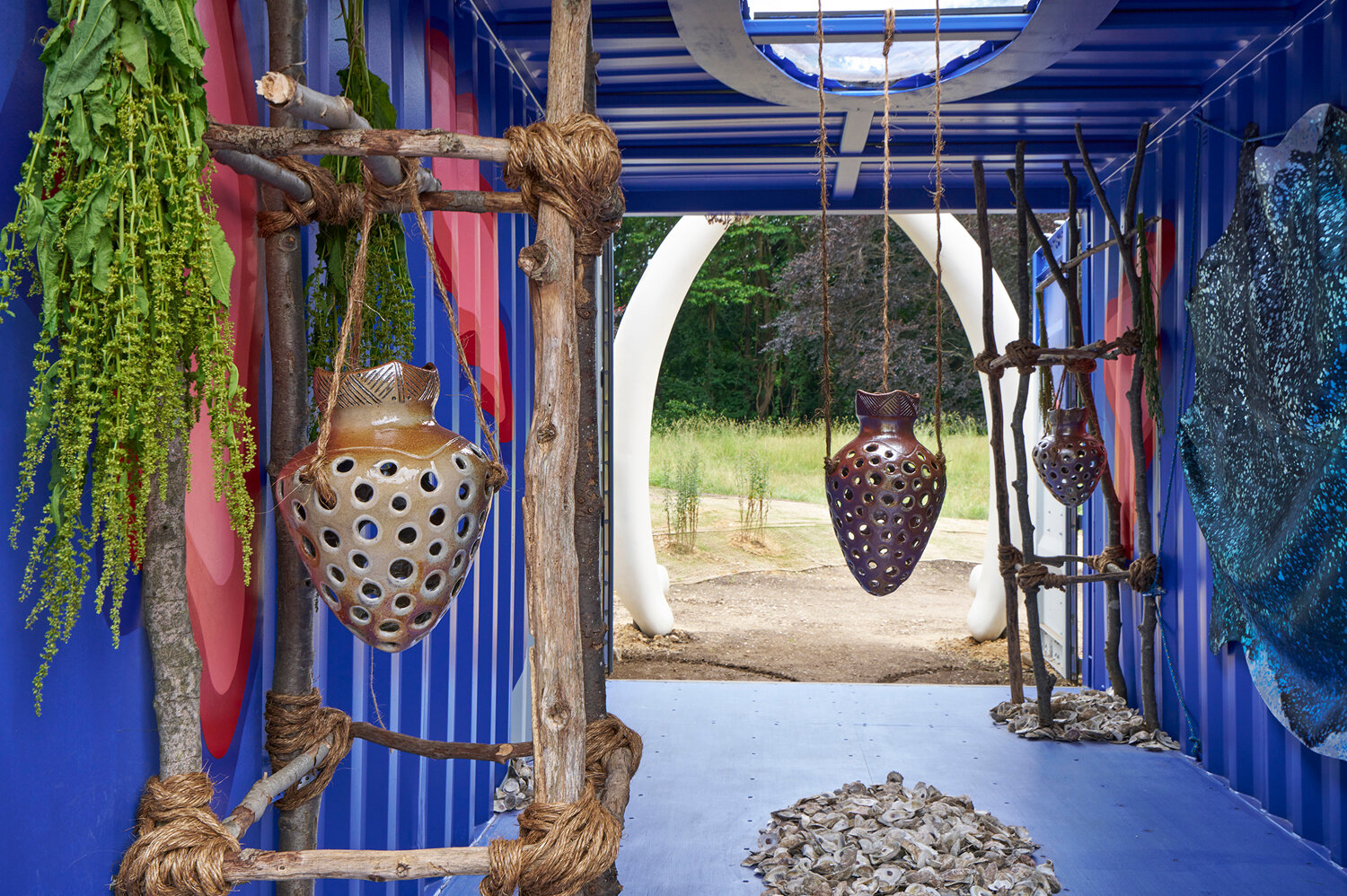
Concurrently with the Heckscher exhibit, Leonard created a site-specific outdoor installation for Planting Fields State Park in Oyster Bay, located in the Taxus Field, on display now through summer 2024.
“We’ve integrated the installation into the landscape,” says Planting Fields’ president and chief executive Gina Wouters. There, Leonard has expanded on her Breach: Logbook 23 concept, with full-sized shipping container integrated into the ground. The shape of the container structure itself is meant to evoke the body of a whale. As you enter through the jaws of a Northern Right Whale, you move through the whale’s body.
“It’s essentially a root cellar, which was a natural refrigeration system and means of food sovereignty for indigenous people,” Wouters says. “She added to that the idea of a shipping container, bringing in the theme of whaling, so important to coastal Indigenous groups, yet abused by colonists. It’s an impressive, ambitious installation because of its scale. It’s wonderful to have this collaboration with the museum, and interpreted into our historic landscape.”

 43.0°,
Partly Cloudy
43.0°,
Partly Cloudy